1. 实现一个 new new 一个对象会发生如下的步骤,基于这些步骤我们来尝试想一下怎么实现它们:
创建或者说事构造一个全新的对象(创建一个空对象);
这个全新的对象会进行 [[Prototype]] 连接(遍历构造函数的 prototype 连接到空对象的 proto 上);
这个对象会被绑定到函数调用的 this(使用 call、apply 来改变构造函数中的 this,并在 new 的阶段执行);
如果函数没有返回其它对象,那么 new 表达式中的函数调用会自动返回这个新对象(判断构造函数有没有返回值)。
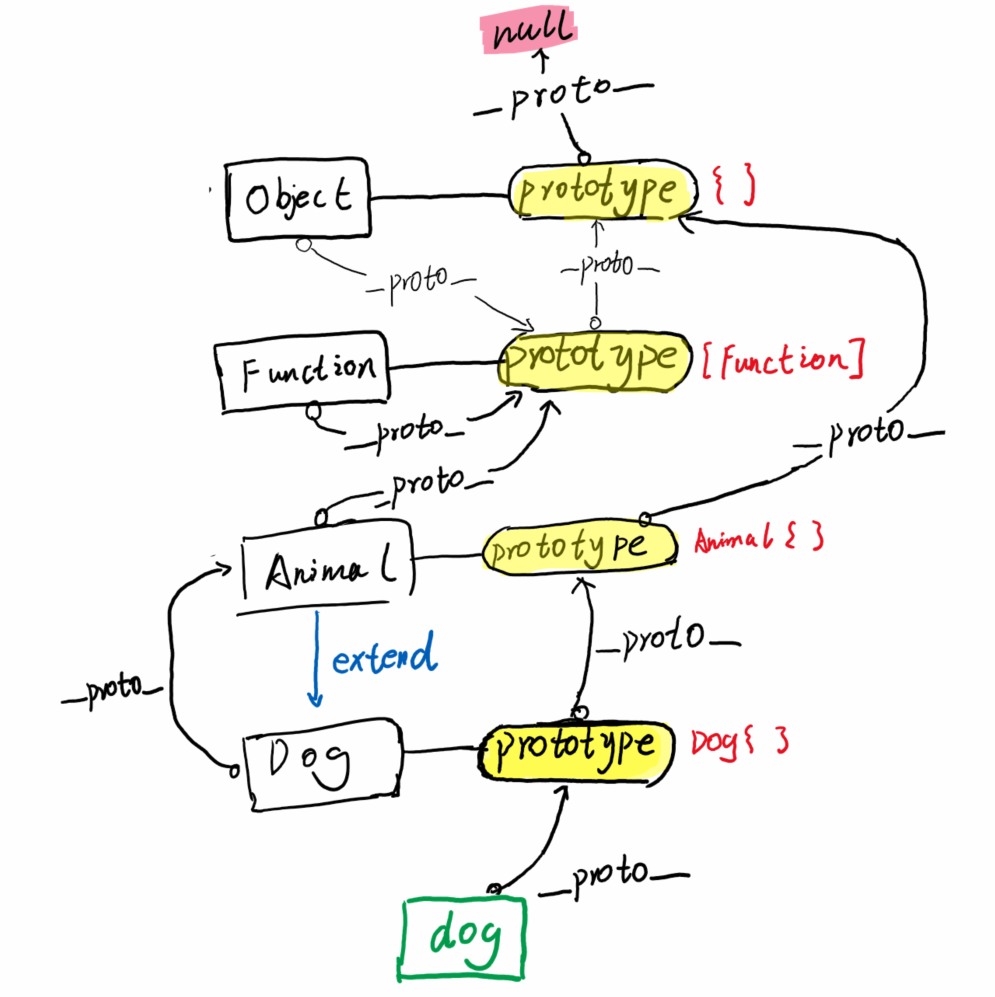
同时,我们来回顾一下这张原型链连接图:
我们要实现一个 createNewObject 方法,让其可以达到如下效果:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 function Dog (name ) { this .name = name; } Dog .prototype sayHi = function ( console .log (`Hi~, my name is ${this .name} ` ); }; Dog .prototype age = 18 ;const newDog = createNewObject (Dog , ["dabai" ]);newDog.sayHi (); console .log (newDog.age );
实现1:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 function createNewObject (constructor, args ) { const result = new Object (); const returnResult = constructor.apply (result, args); if (returnResult instanceof Object ) { return returnResult; } result.__proto__ = { constructor }; Object .keys (constructor.prototype forEach ((prototypeKey ) => { const targetPrototype = constructor.prototype Object .defineProperty (result.__proto__ , prototypeKey, { writable : false , value : targetPrototype, }); }); return result; }
(1) 其实在创建一个空对象时候,可以写为 result = {} 或者 result = new Object(),甚至如果你想创建一个真正意义上的纯空的对象的话,可以使用 result = Object.create(null),但是要注意的是 Object.create(null) 的方法在 Nodejs 环境下,创建的对象无法改写 proto ,这就导致我们无法去连接构造函数的 prototype。
实现2:
我们其实可以利用 Object.create() 来实现,其含义为:
Object.create() 方法创建一个新对象,使用现有的对象来提供新创建的对象的proto
那么实现一个 new 方法就可以改写为:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 function createNewObject (constructor, args ) { const result = Object .create (constructor.prototype const returnResult = constructor.apply (result, args); if (returnResult instanceof Object ) { return returnResult; } return result; }
2. 实现 call apply 方法
https://github.com/mqyqingfeng/Blog/issues/11
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 Function .prototype call2 = function (context ) { var context = context || window ; context.fn = this ; var args = []; for (var i = 1 , len = arguments .length ; i < len; i++) { args.push ('arguments[' + i + ']' ); } var result = eval ('context.fn(' + args +')' ); delete context.fn return result; } var value = 2 ;var obj = { value : 1 } function bar (name, age ) { console .log (this .value ); return { value : this .value , name : name, age : age } } bar.call2 (null ); console .log (bar.call2 (obj, 'kevin' , 18 ));
3. bind 的实现
https://www.cnblogs.com/echolun/p/12178655.html
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 Function .prototype bind_ = function (obj ) { if (typeof this !== "function" ) { throw new Error ("Function.prototype.bind - what is trying to be bound is not callable" ); }; var args = Array .prototype slice .call (arguments , 1 ); var fn = this ; var fn_ = function ( var bound = function ( var params = Array .prototype slice .call (arguments ); fn.apply (this .constructor === fn ? this : obj, args.concat (params)); console .log (this ); }; fn_.prototype prototype bound.prototype new fn_ (); return bound; };
4. 实现一个深克隆
https://juejin.cn/post/6844903929705136141#heading-8
重点:
使用递归实现深拷贝
基础要实现 Object 和 Array 的拷贝
创建一个 Map 来存放已经拷贝过的对象,防止循环引用
使用 Object.prototype.toString 来判断拷贝对象的
对于 Map、Set 要遍历拷贝
对于 Boolean、Number、String、Error 要调用对应的构造函数来拷贝
对于 RegExp 和 Symbol 要单独特殊处理
对于函数来说,可以通过 toString 将函数转为字符串,然后使用目标函数是否有 prototype 来判断其是箭头函数还是普通函数:
箭头函数可以直接返回 eval(functionString) 的执行结果来拷贝函数
对于普通函数,需要利用正则解析函数的参数位以及函数体,再利用 new Function(…paramArr, functionBody) 来克隆一个函数
JSON.stringify 的局限性:
仅能正确克隆基础类行,以及克隆对象、数组
对于无法拷贝的对象(这些对象通常在 JSON 中没有有效概念),如:Map、Set、RegExp、Function,会返回一个空对象 {}
对于 undefined 会直接忽略该键值
会将 NaN 转为 null
会将 Date 转为时间字符串
无法序列化的对象,如 BigNumber,会直接报错
对于循环引用会报错
基础版(仅实现了 1~3):
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 function clone (target, map = new Map () ) { if (typeof target === 'object' ) { let cloneTarget = Array .isArray (target) ? [] : {}; if (map.get (target)) { return map.get (target); } map.set (target, cloneTarget); for (const key in target) { cloneTarget[key] = clone (target[key], map); } return cloneTarget; } else { return target; } };
5. 实现继承
https://developer.mozilla.org/zh-CN/docs/Web/JavaScript/Reference/Global_Objects/Object/create
ES5 环境下,可以使用 SubClass.prototype = Object.create(ParentClass) 来连接父类的原型链:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 function Shape ( this .x = 0 ; this .y = 0 ; } Shape .prototype move = function (x, y ) { this .x += x; this .y += y; console .info ('Shape moved.' ); }; function Rectangle ( Shape .call (this ); } Rectangle .prototype Object .create (Shape .prototype Rectangle .prototype constructor = Rectangle ;var rect = new Rectangle ();console .log ('Is rect an instance of Rectangle?' , rect instanceof Rectangle ); console .log ('Is rect an instance of Shape?' , rect instanceof Shape ); rect.move (1 , 1 );
如果你希望能继承到多个对象,则可以使用混入的方式。
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 function MyClass ( SuperClass .call (this ); OtherSuperClass .call (this ); } MyClass .prototype Object .create (SuperClass .prototype Object .assign (MyClass .prototype OtherSuperClass .prototype MyClass .prototype constructor = MyClass ;MyClass .prototype myMethod = function ( };
更低版本的 ES 标准下,可以使用 new 关键字的特性来模拟 Object.create:
1 2 3 4 5 function objectCreate (o ) { function F ( F.prototype return new F (); }